Too good to be true? How to check if the health products you get online are genuine

KUALA LUMPUR, June 18 — With the increasing demand for health supplements, consumers face ever greater risks of unscrupulous vendors using e-commerce to pass off counterfeits as heavily discounted products.
Also riding on the interest in health and wellbeing in the post-Covid 19 era are sellers marketing products catering to this demand, but without the necessary consumer safety and quality controls.
By law, all pharmaceutical products sold in Malaysia, including health supplements and traditional products, must be registered with the Drug Control Authority (DCA) — an executive body established under the Control of Drugs and Cosmetics Regulations 1984 — before being marketed locally.
But how does one determine which are genuine and which are the fake?
Fret not, Malay Mail has prepared this guideline courtesy of the Health Ministry via the National Pharmaceutical Regulatory Agency (NPRA) to help consumers identify a product's legitimacy.
Verify at first sight
Firstly, registered pharmaceutical and natural products as well as health supplements must bear a security label (hologram) that is visible without having to open the packaging.
First introduced (then known as Meditag) in 2005, these holograms — called FarmaTag as of September 2019 — assist consumers in identifying registered health products visually.

The hologram sticker has been mandatory in Malaysia since 2005. — Picture by Choo Choy May
Security labelling is mandatory as provided under Regulation 8(1) of the Control of Drugs and Cosmetics Regulations 1984, with the hologram production overseen by a single ministry-appointed supplier.
According to the NPRA’s existing guideline, only licensed manufacturers and importers of pharmaceutical, traditional medicine and health supplement products may purchase these labels; while local manufacturer, repacker for products imported in bulk or the importer shall be responsible for affixing the hologram onto the individual unit packs.
This means if a product does not have the hologram, it is likely unregistered, has not passed inspection, or a counterfeit.
Measuring just 8mm by 18mm, the FarmaTag has various security features that can be seen by both consumers and pharmaceutical enforcers to determine the legitimacy of products registered with the Health Ministry.
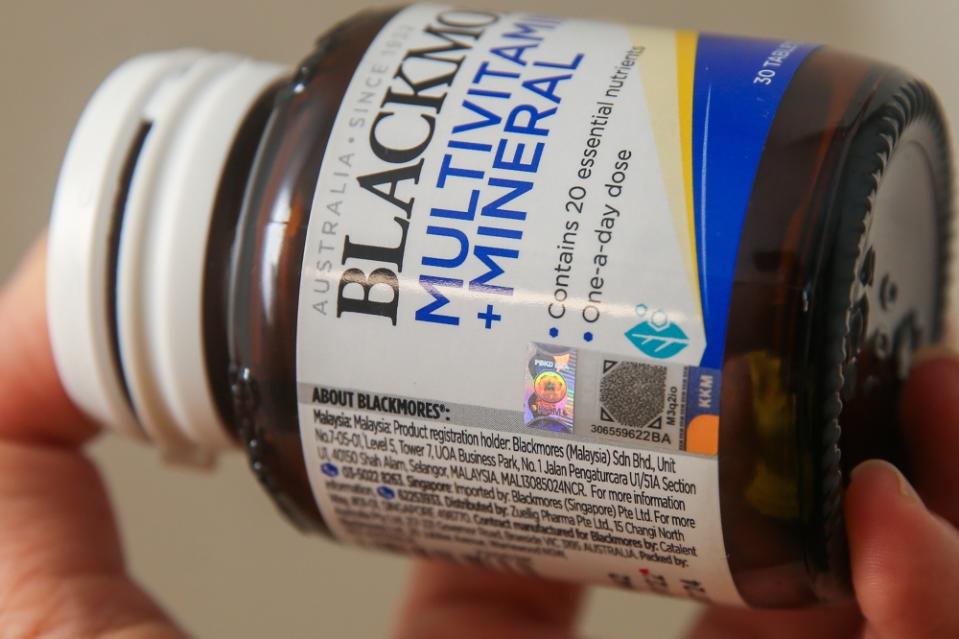

The hologram contains a QR code and serial number that can be used to verify its authenticity. — Picture by Choo Choy May
Examples of the security feature includes a holographic image depicting two acronyms — PBKD and DCA, which stand for Pihak Berkuasa Kawalan Dadah (the Malay name for the DCA) — a ministry-issued QR Code, a gradient design, and serial and identification numbers.
Consumers can also verify the authenticity of the FarmaTag by using the FarmaChecker mobile application to scan the QR code or type in its serial number.
They can also check the product’s registration number at the NPRA’s official website.
Apart from the hologram, DCA-registered products have another security feature in the form of the registration number printed on its label or package. This starts with MAL followed by eight numbers and ending with the letter T, A, X or N (for example, MAL12345678X).
The letter after the eight numbers denotes the product’s category: controlled medicine or prescription drugs (A), over-the-counter or non-prescription drug (X), traditional medicine (T), or health supplements (N).
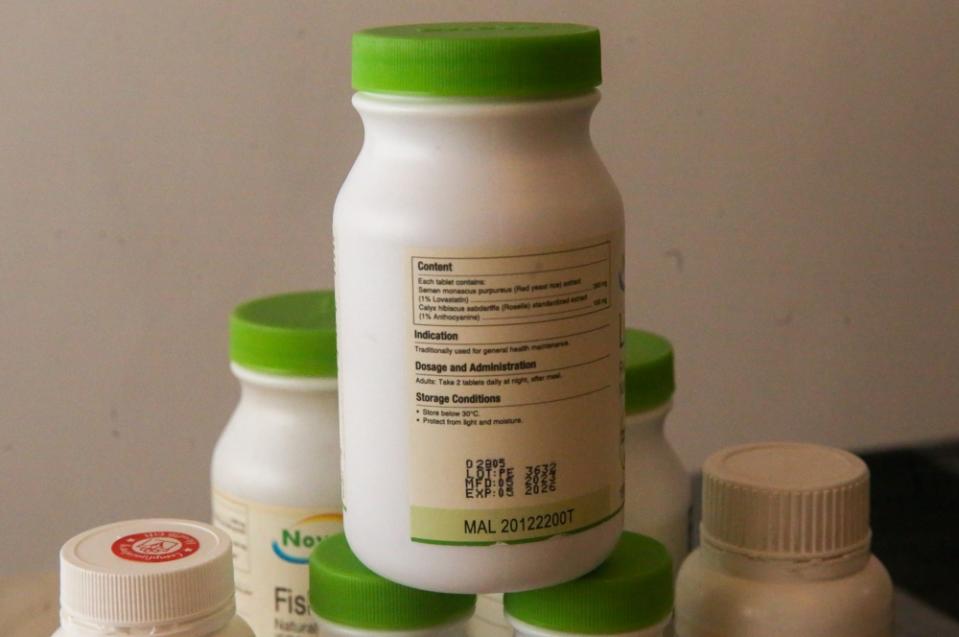
The final letter in the registration number identifies that category of the health product. — Picture by Choo Choy May
To ensure compliance, those found selling or supplying any unregistered health products (including failure to implement the hologram) will be in violation of Regulation 7(1)(a) of the Control of Drugs and Cosmetics Regulations 1984.
Upon conviction, individuals face a fine of up to RM25,000 or imprisonment of up to three years or both for their first offence; and a fine of up to RM50,000 or imprisonment of up to five years or both for subsequent offences.
Corporate bodies will face a fine of up to RM50,000 for their first offence and RM100,000 for their subsequent offences.
It pays to be vigilant
The NPRA released in October 2023 an advisory on the risk and dangers consumers face when purchasing health products and supplements online, as the safety, quality and efficacy of such products are unknown.
Such risks are even higher with counterfeit products, which may include contamination with heavy metal elements (mercury, arsenic) and undeclared dosing with controlled substances (sildenafil, sibutramine) that can be life-threatening if consumed without proper medical supervision.
Sildenafil is used to treat men who have erectile dysfunction while sibutramine is a compound widely used in weight loss products.
In reminding consumers to be vigilant and take appropriate measures in purchasing medicine online, NPRA said this was to avoid falling victim to irresponsible and unscrupulous sellers.
For any information or complaints relating to the sale and supply of counterfeit medicines, consumers are advised to do so at the Health Ministry’s Public Complaints Management System (SISPAA) website here or any Pharmacy Enforcement state branches nationwide.