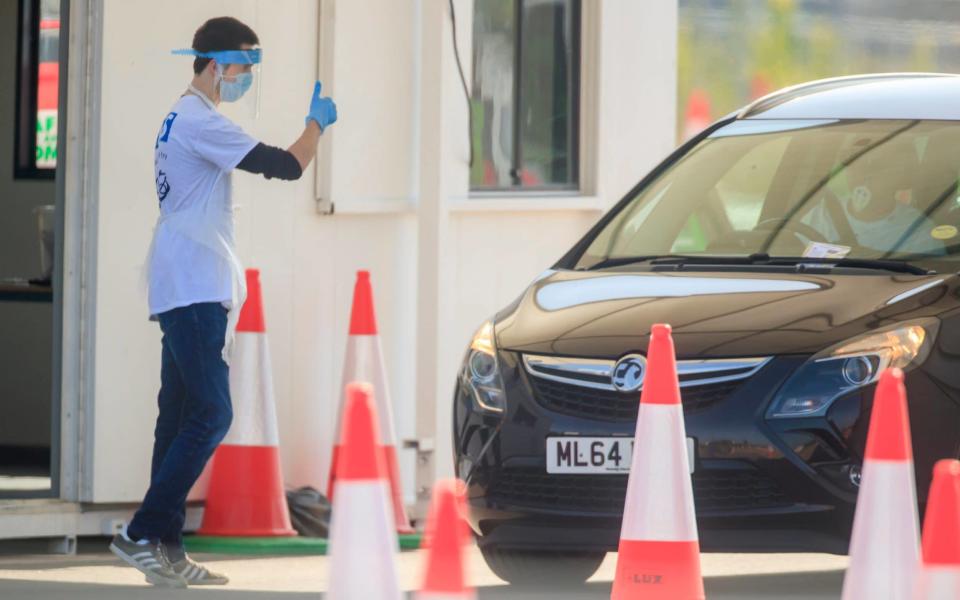
NHS Test and Trace: is the UK equipped to keep the coronavirus in check?

From syphilis to tuberculosis, contact tracing has been a weapon in the arsenal of public health officials for almost 100 years.
And since coronavirus took hold, it has been used very effectively to strangle the outbreak in a number of countries, from Singapore to New Zealand.
It was even used at the beginning of the outbreak in the UK, in March, although as cases spiralled it was dropped - arguably unwisely - as it became impracticable.
But the launch on Thursday of the government's 'Test and Trace' programme marks a new phase in the fightback as the lockdown begins to lift, one the World Health Organization has said is "crucial" in getting societies back to anything like normal.
And luckily for the UK government, after a dubious launch day with crashed websites, unprepared local partners and the admission that it would be at least another month before the system was fully operational, experts said it didn't have to be perfect to be worthwhile.
"While I would like it to be as good as possible, it doesn't have to be perfect," said Professor Mark Woolhouse, from the Infectious Disease Epidemiology department at the University of Edinburgh.
"The sort of target, the number that is talked about is if we could reliably trace 80 per cent of contacts for enough cases, that would make inroads. No-one has to go to ridiculous extremes."
How will it work?
The basic idea is that any coronavirus sufferer is identified and tested, and then anyone they have been in prolonged contact with is in turn contacted by the NHS contact tracing team, and urged to self-quarantine for up to 14 days. That means not going out at all, even for exercise, the government has said, and even minimising contact within households if possible - although there has been little guidance about what that will mean practically, or if any alternative accommodation will be provided. In some other countries, hotels have been used as quarantine centres.
At the moment, the system - described as "analogue" rather than digital by some experts - does not involve the previously much-vaunted app, and relies instead on individuals, their memories, and phone calls, texts and emails from some 25,000 contact tracers hired by the government, supported by local public health teams in complex cases.
The challenges
Dr Emily Gurley at the John Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in the United States, who wrote the training for contact tracers in New York state, said the challenge was "daunting".
"Do you have enough people, are you fast enough, are you finding enough cases, are you able to find and contact them in a timely way, are you able to find their contacts, and did you find enough of them?" she said.
"The effort is daunting but doable. We just have to ramp it up way beyond what we're used to doing."
There are a host of other questions too: what exactly does a "contact" mean, and how will coronavirus sufferers remember who exactly they met - particularly as society begins to open up again? How will contact tracing teams find contacts, particularly in situations where the initial case cannot or will not provide their details? And if the system is, as it currently remains, "voluntary" rather than mandatory, will it actually work?
Contacts
The government has some answers. For example, following World Health Organization guidelines, a "contact" is someone who has been in close contact, usually indoors, with a confirmed coronavirus case for longer than 15 minutes.
In normal life, Dr Scott McLachlan, founding fellow of the Australasian Institute for Digital Health at Queen Mary University London, said the average person is only going to remember around 35 per cent of their daily interactions, although at the moment lockdown measures mean it would be much higher.
For contact tracing to work, he says, an app needs to be part of the solution - and the government agrees, although the app is not ready yet.
"We are trying to adapt a solution for a different disease," he said. "For example, a sexually transmitted disease - you know the three people you had sex with in the last few months, it's easy to find them and trace them. With coronavirus you can't know who you gave it to. So it's like trying to use a square in the axle of your car."
In other countries, such as Germany, some bars have reopened with forms for patrons to fill in so they can be tracked if another customer later tests positive for coronavirus.
In the UK, even if someone suffering with coronavirus did remember their contacts, they may be either unwilling or unable to pass on contact details for them - and it is not clear how exactly the UK contact tracers will then find them, although they can then contact business owners, for example airlines, to try to reach people.
Speed
There's another issue: speed. All of the experts agreed that in order for contact tracing to work, it has to be fast. In fact, Professor Woolhouse said speed is actually more important than making sure to track down every last contact.
"The real benefit of this is catching infections before they become infectious, before they have symptoms and can infect others. That would really help but it depends on acting fast. If it is too slow, if, for instance, it takes a week, it's not going to do much," he said.
That's quite the challenge: firstly, it involves someone with suspected symptoms declaring themselves, getting tested, and getting the results quickly. At the moment, test results are taking between 24 and 48 hours, which Professor Woolhouse says is too slow. At that point the tracing team then have to talk to that confirmed case, then find their contacts, and then talk to them.
It is issues like this that made the Royal Society's Delve group (Data Evaluation and Learning for Viral Epidemics) suggest that, at best, contact tracing now could reduce the number of new cases by 15 per cent. If the response is much slower, it would go down to 5 per cent.
"It's worth doing, but it's not suddenly a magic bullet," said Professor Woolhouse, suggesting that measures like hand washing would remain critical.
"It depends partly on how well it's carried out and partly on how well people adhere to it. But every case it prevents is a chain of infection that is broken."
Compliance
That's another major issue: how well people adhere to it.
In a pilot study in Sheffield, set up by a group of retired doctors and public health officials, only one-third of the people identified as "contacts" agreed to self-isolate. Some couldn't be found, and while others were generally compliant, in many cases, their employers were not - and so they had to keep going to work.
The Department of Health and Social Care said that employers must support self-isolation and statutory sick pay would be available.
There are other issues: in the United States, contact tracing efforts were paused in Washington State after many simply did not answer the phone to an unknown number.
For data protection reasons in the UK, contact tracers will not be able to provide much information about how or where people got infected - which could affect whether they will follow the rules.
Challenge lifting restrictions even with arguably world’s best Test-Isolate-Contact system in place. Virus not changed remains highly infectious, human population remains largely susceptible.Probable that lifting restrictions will lead to increase in cases https://t.co/S8n5DuOYdc
— Jeremy Farrar (@JeremyFarrar) May 28, 2020
And tests will only be available for those with symptoms, meaning that many healthy people will be asked to lock themselves indoors for two weeks, based only on the government's advice, just as things are getting going again.
Lastly, even the behavioral scientists advising the government said there was one major issue which remained in whether people would stick to the tough demands of a test and trace scheme: the furore over whether Dominic Cummings, Boris Johnson's closest advisor, broke the lockdown rules with a trip to Durham.
"At every level this [track and trace] is a difficult thing to do," said Professor Stephen Reicher, who advises the government on behavioural responses during a pandemic. "But the good news of the pandemic so far have been the remarkable levels of compliance, even quite heroic compliance. And people haven't done it because they were told to; they did it because they believed in it. But that sense of shared identity which often emerges in disasters - we like to say the 'Blitz spirit', but it's not unusual - is a fragile thing, and it's easy to undermine if you think others are not abiding by it."
He fears that the prime minister's defence of Mr Cummings, that it was ok to act on instinct to support your family - as many others have not in order to remain compliant with the lockdown rules - has broken the bond of trust at a moment when it was arguably more important to maintain it than ever before.
"As long as Dominic Cummings stays in post, that comes at a considerable cost, I think, to the authority of the government at a time when we need good leadership to unite us," he said.
Even small changes in compliance made big differences in infections and deaths, he said, as modelling over compliance with lockdown measures has shown.
"We play around with adherence and trust at our peril," he said.

